With its varied topography and Mediterranean climate, California is home to a remarkable diversity of native plants that have adapted to thrive in the state's unique conditions. From coastal bluffs and deserts to mountains and forests, California boasts an array of ecosystems that support countless plant species.
In this article, we will examine some of the most common native plants found in California, highlighting their characteristics, uses, and ecological significance.
Read Next
- 1. California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica)
- 2. Coast Live Oak (Quercus agrifolia)
- 3. Toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia)
- 4. California Lilac (Ceanothus spp.)
- 5. Manzanita (Arctostaphylos spp.)
- 6. California Sagebrush (Artemisia californica)
- 7. California Buckwheat (Eriogonum fasciculatum)
- 8. Sticky Monkeyflower (Diplacus aurantiacus)
- 9. California Fuchsia (Epilobium canum)
- 10. Matilija Poppy (Romneya coulteri)
- 11. California Sycamore (Platanus racemosa)
- 12. Giant Sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum)
- 13. Western Redbud (Cercis occidentalis)
- 14. California Wild Grape (Vitis californica)
- 15. White Sage (Salvia apiana)
- Conclusion
- 💬 Feedback
1. California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica)
The California poppy, the state's official flower, is a bright orange annual that blooms from February to September. Found in grasslands, coastal regions, and deserts, this drought-tolerant wildflower is a crucial source of nectar for pollinators and a beloved symbol of the Golden State.
2. Coast Live Oak (Quercus agrifolia)
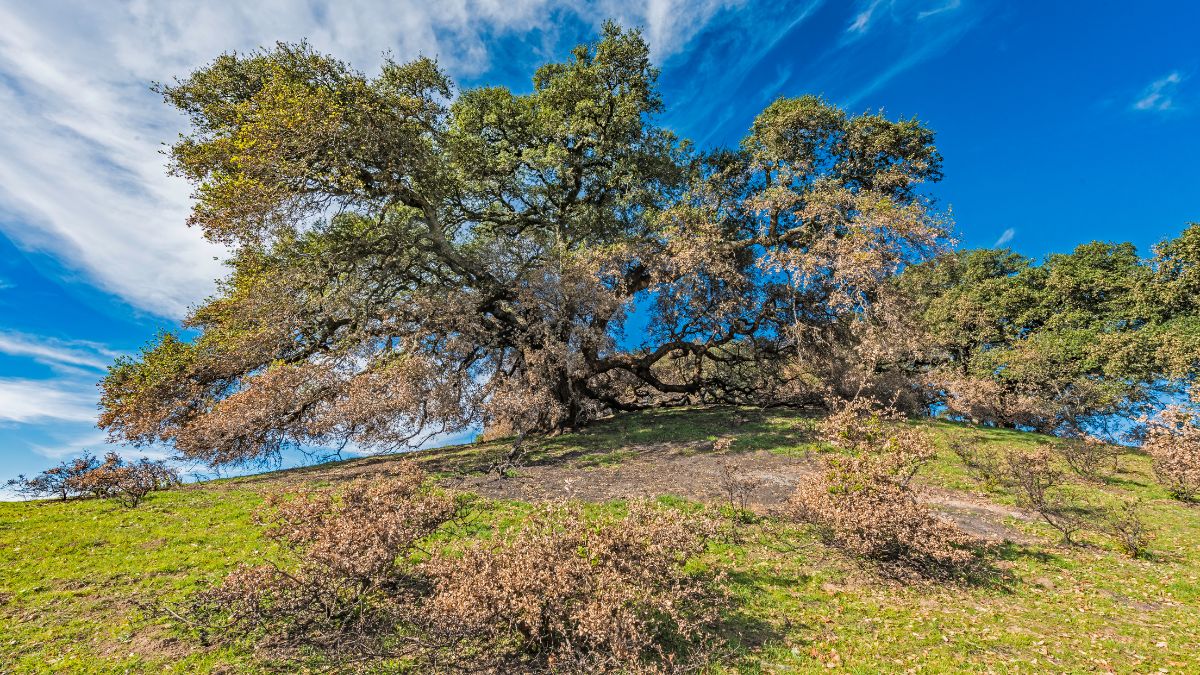



The coast live oak is an evergreen tree native to coastal California and the southern part of the state. With its twisted branches and dense canopy, this iconic tree provides habitat and food for numerous wildlife species. The acorns were a staple food for Native Californians, who also used the tree's bark for medicinal purposes.
3. Toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia)
Also known as California holly or Christmas berry, toyon is an evergreen shrub that produces clusters of white flowers in summer and bright red berries in winter. The berries are an essential food source for birds and were traditionally used by Native Californians for food and medicine.
4. California Lilac (Ceanothus spp.)
California lilac, a genus encompassing over 50 species, is a group of evergreen and deciduous shrubs found throughout the state. Known for their vibrant blue, purple, or white flowers, these drought-tolerant plants are an essential source of nectar for native bees and butterflies.
5. Manzanita (Arctostaphylos spp.)
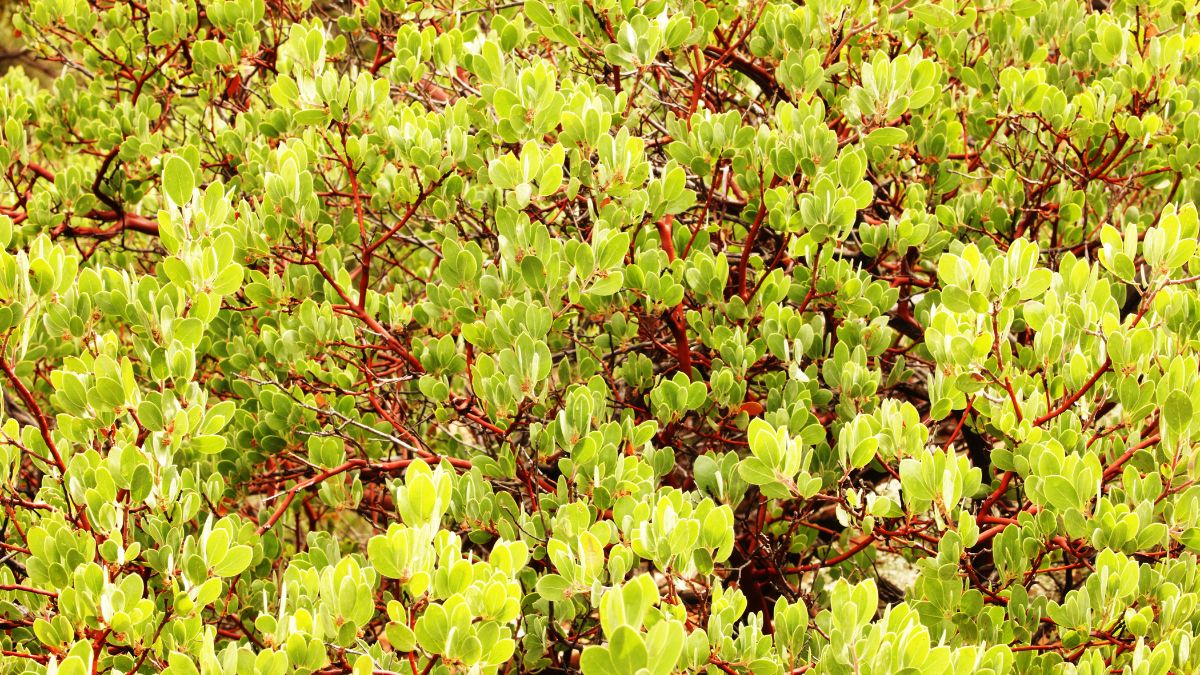



Manzanita, with its distinctive red bark and twisted branches, is a group of evergreen shrubs and small trees native to California. The small, bell-shaped flowers provide nectar for hummingbirds and bees, while the berry-like fruits are a food source for birds and mammals. Manzanita is also a popular choice for drought-tolerant landscaping.
6. California Sagebrush (Artemisia californica)
California sagebrush, also known as coastal sage, is an aromatic, drought-tolerant shrub found in coastal sage scrub and chaparral ecosystems. The plant's grayish-green leaves provide cover for birds and small mammals, while its strong scent is thought to deter herbivores. Native Californians used the plant for medicinal purposes.
7. California Buckwheat (Eriogonum fasciculatum)
This drought-tolerant perennial produces clusters of tiny, white-to-pink flowers that attract bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Found in chaparral, coastal sage scrub, and grassland ecosystems, California buckwheat is an important food source for native wildlife and a popular choice for native plant gardens.
8. Sticky Monkeyflower (Diplacus aurantiacus)
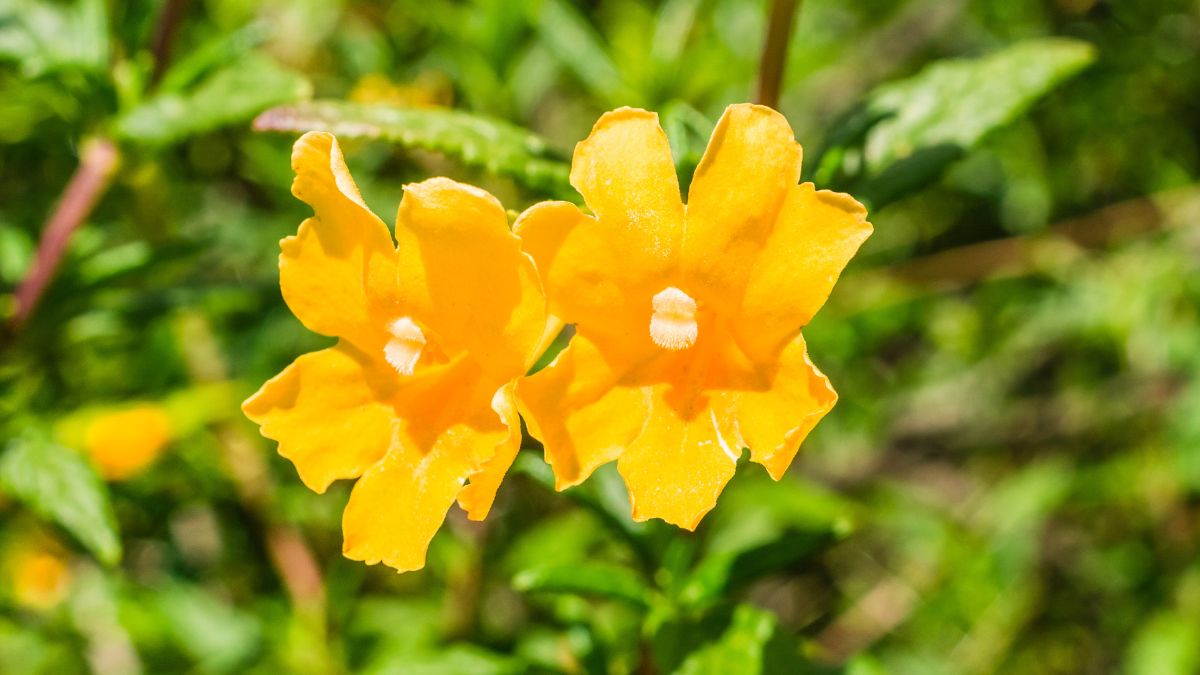



The sticky monkeyflower is a perennial shrub with tubular, orange-to-yellow flowers that attract hummingbirds and butterflies. Named for its sticky leaves, this plant is found in chaparral, coastal sage scrub, and woodland habitats. Native Californians used the plant for medicinal purposes, including treating skin conditions and digestive issues.
9. California Fuchsia (Epilobium canum)
California fuchsia, also known as hummingbird trumpet, is a perennial with tubular, red-to-orange flowers that bloom from July to November. As the name suggests, the bright flowers are a favorite of hummingbirds, making this plant an excellent addition to wildlife gardens. California fuchsia is drought-tolerant and well-suited to the state's dry conditions.
10. Matilija Poppy (Romneya coulteri)
The Matilija poppy, with its large, white, crepe-paper-like flowers and bright yellow centers, is a striking native plant found in southern California. This perennial shrub blooms from May to July and is drought-tolerant, making it an excellent choice for xeriscaping. The flowers also attract pollinators, including bees and butterflies.
11. California Sycamore (Platanus racemosa)
This large, deciduous tree is native to California's riparian areas and canyons. The California sycamore is known for its distinctive peeling bark, large palmate leaves, and round seed balls. This tree provides important habitat for birds, and its leaves are a food source for native butterfly caterpillars.
12. Giant Sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum)
The giant sequoia, one of Earth's largest and oldest living organisms, is native to California's Sierra Nevada mountains. These towering trees can live for thousands of years and are an awe-inspiring symbol of the state's natural heritage. The giant sequoia provides habitat for a variety of wildlife, including birds and small mammals.
13. Western Redbud (Cercis occidentalis)



The western redbud is a small, deciduous tree that produces vibrant pink blossoms in early spring. Native to California's foothills and valleys, this tree is drought-tolerant and provides food and habitat for birds and butterflies. The western redbud's bark was traditionally used by Native Californians for basketry and cordage.
14. California Wild Grape (Vitis californica)
California wild grape is a deciduous vine that produces clusters of small, edible grapes in late summer. Found in riparian areas and along streambanks, this native plant is a valuable food source for birds and mammals. The vine is also used for erosion control and can be trained to grow on arbors and fences.
15. White Sage (Salvia apiana)
White sage is an aromatic, evergreen shrub found in southern California's chaparral and coastal sage scrub ecosystems. Known for its grayish-white leaves and tall flower stalks, this plant is prized for its strong scent and is often used in smudging rituals. White sage is also drought-tolerant and attracts bees and other pollinators.
Conclusion
The diverse native plants of California contribute to the state's rich natural heritage and play vital roles in maintaining healthy ecosystems. These plants offer beauty and sustenance for pollinators and wildlife and provide valuable resources for humans. By preserving and cultivating native plants, Californians can help ensure the vitality and resilience of their state's unique flora for generations to come.

Comments
No Comments