The state of Colorado is known for its diverse terrain and variable climate, housing an array of ecosystems from grasslands and deserts to forests and alpine tundras. The native plants within these habitats have evolved to adapt to these conditions, which is vital in sustaining the state's biodiversity.
This article shows some of the most common native plants found in Colorado, highlighting their characteristics, uses, and ecological importance.
Read Next
- 1. Colorado Blue Columbine (Aquilegia Coerulea)
- 2. Ponderosa Pine (Pinus Ponderosa)
- 3. Blue Grama (Bouteloua Gracilis)
- 4. Indian Paintbrush (Castilleja Spp.)
- 5. Rocky Mountain Juniper (Juniperus Scopulorum)
- 6. Yucca (Yucca Spp.)
- 7. Plains Prickly Pear (Opuntia Polyacantha)
- 8. Rocky Mountain Bee Plant (Cleome Serrulata)
- 9. Showy Milkweed (Asclepias Speciosa)
- 10. Bitterbrush (Purshia Tridentata)
- 11. Quaking Aspen (Populus Tremuloides)
- 12. Mountain Mahogany (Cercocarpus Ledifolius)
- 13. Cliffrose (Purshia Stansburiana)
- 14. Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla Patens)
- 15. Sagebrush (Artemisia Tridentata)
- Conclusion
- 💬 Feedback
1. Colorado Blue Columbine (Aquilegia Coerulea)
The Colorado blue columbine, the state's official flower, is a perennial herb that thrives in woodlands and meadows. Its delicate, blue-and-white blossoms appear from April to August, attracting pollinators. The plant also has historic medicinal uses.
2. Ponderosa Pine (Pinus Ponderosa)



The ponderosa pine is a large, towering tree common in Colorado's montane and foothill ecosystems. This evergreen tree provides a habitat for many bird species, and its seeds are a food source for wildlife.
3. Blue Grama (Bouteloua Gracilis)
Blue grama, the state grass of Colorado, is a perennial grass native to the shortgrass prairies. Tolerant of drought and a variety of soil conditions, blue grama is important for soil stabilization and provides forage for grazing animals.
4. Indian Paintbrush (Castilleja Spp.)
Indian paintbrush, known for its bright red, orange, or yellow bracts, is a perennial wildflower. This plant often grows in open spaces and forests, its vibrant colors attracting pollinators throughout the growing season.
5. Rocky Mountain Juniper (Juniperus Scopulorum)
This evergreen tree or shrub, found in the mountains and plateaus of Colorado, is characterized by its dense, blue-green foliage. Its berries are a food source for birds and mammals, and its wood has been used for building.
6. Yucca (Yucca Spp.)



Yucca plants, with their sword-like leaves and tall flower spikes, are native to the semi-arid regions of Colorado. These plants are known for their use in making soaps and cordage and for their edible fruits and flower petals.
7. Plains Prickly Pear (Opuntia Polyacantha)
A common sight in Colorado's lower elevations, the plains prickly pear cactus blooms with vibrant yellow or pink flowers in summer. This plant's fruits and young pads are edible, and it's an important resource for desert wildlife.
8. Rocky Mountain Bee Plant (Cleome Serrulata)
This annual wildflower, with its bright pink flowers, blooms from June to September in disturbed sites and dry prairies. It is an important source of nectar and pollen for bees and other pollinators.
9. Showy Milkweed (Asclepias Speciosa)
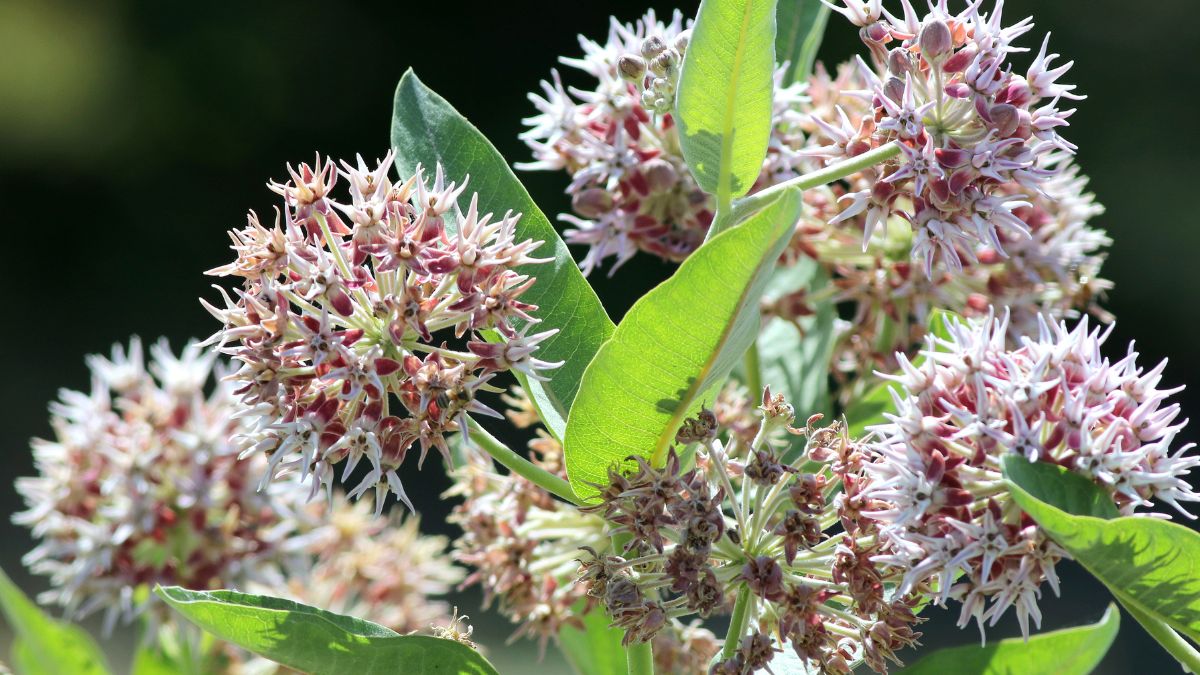



Showy milkweed, a perennial herb, grows in moist habitats across Colorado. Its pinkish-purple flowers are an important food source for monarch butterflies, while its milky sap has been used in traditional medicine.
10. Bitterbrush (Purshia Tridentata)
Bitterbrush is an evergreen shrub that thrives in Colorado's semi-arid environments. It produces small yellow flowers, and its leaves, twigs, and seeds provide food for various wildlife, including deer and birds.
11. Quaking Aspen (Populus Tremuloides)
The quaking aspen, a deciduous tree named for its shimmering leaves, is a dominant species in Colorado's mountain landscapes. This tree provides habitat for a variety of wildlife, from birds to mammals.
12. Mountain Mahogany (Cercocarpus Ledifolius)
Mountain mahogany is an evergreen shrub common in Colorado's foothills and lower mountain areas. It's known for its hardwood and feathery seed plumes, while its leaves and seeds serve as food for wildlife.
13. Cliffrose (Purshia Stansburiana)
Cliffrose, a resilient shrub, thrives in dry, rocky areas of western Colorado. It produces fragrant white flowers, and its seeds, leaves, and bark provide nourishment for wildlife and were traditionally used for medicinal purposes.
14. Pasqueflower (Pulsatilla Patens)
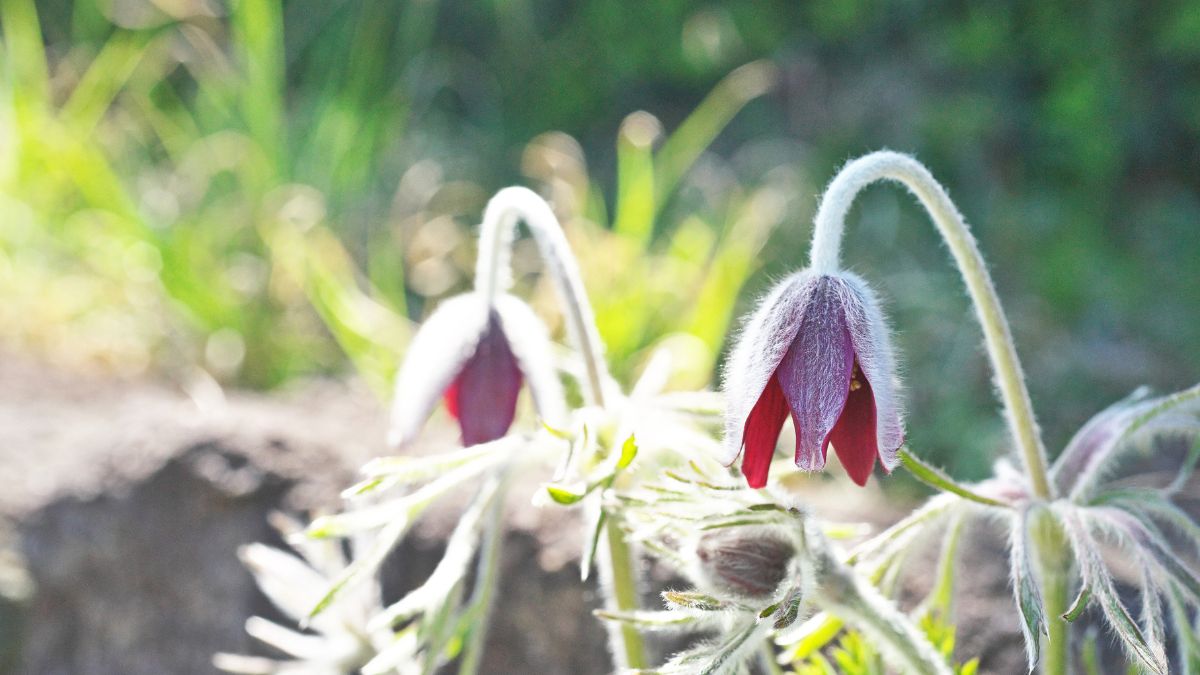



With its distinctive purple flowers and feathery seed heads, the pasqueflower is one of the first wildflowers to bloom in spring. Found in grasslands and open woodlands, it attracts pollinators and has traditional medicinal uses.
15. Sagebrush (Artemisia Tridentata)
Sagebrush, a dominant plant in Colorado's western landscapes, is an aromatic shrub with silver-gray leaves. It provides cover and food for wildlife, and Native Americans used it for a variety of medicinal purposes.
Conclusion
Colorado's native plants are integral to the state's rich biodiversity and ecological stability. These species offer a glimpse into the state's natural heritage and serve as vital resources for pollinators, wildlife, and humans.
Conserving and cultivating these native plants can ensure the continued health and resilience of Colorado's unique flora and fauna for generations to come.

Comments
No Comments